Everything You Should Know About Rotator Cuff Tears

Medically Reviewed By:

Rotator cuff tears happen when the tendons in the shoulder suffer wear or injury from overuse, trauma, or age-related changes. This condition can lead to pain, weakness, and limited movement, impacting daily activities like lifting or reaching.
Many people use medications to manage symptoms. A 2024 study indicates that shoulder injuries are frequently associated with increased opioid use. However, while medications can offer symptom relief, they may not address the root cause of the shoulder damage and could potentially lead to surgery as the condition worsens.
Procedures using Regenexx lab processes to treat rotator cuff tears utilize interventional orthobiologics to support the body’s natural healing process. The Regenexx approach offers people a less invasive alternative that reduces the need for shoulder surgery or long-term use of prescription drugs.
Understanding The Anatomy Of The Shoulder
The shoulder is one of the most complex and mobile joints in the body. It enables various movements essential for everyday tasks, like lifting, pushing, and reaching.
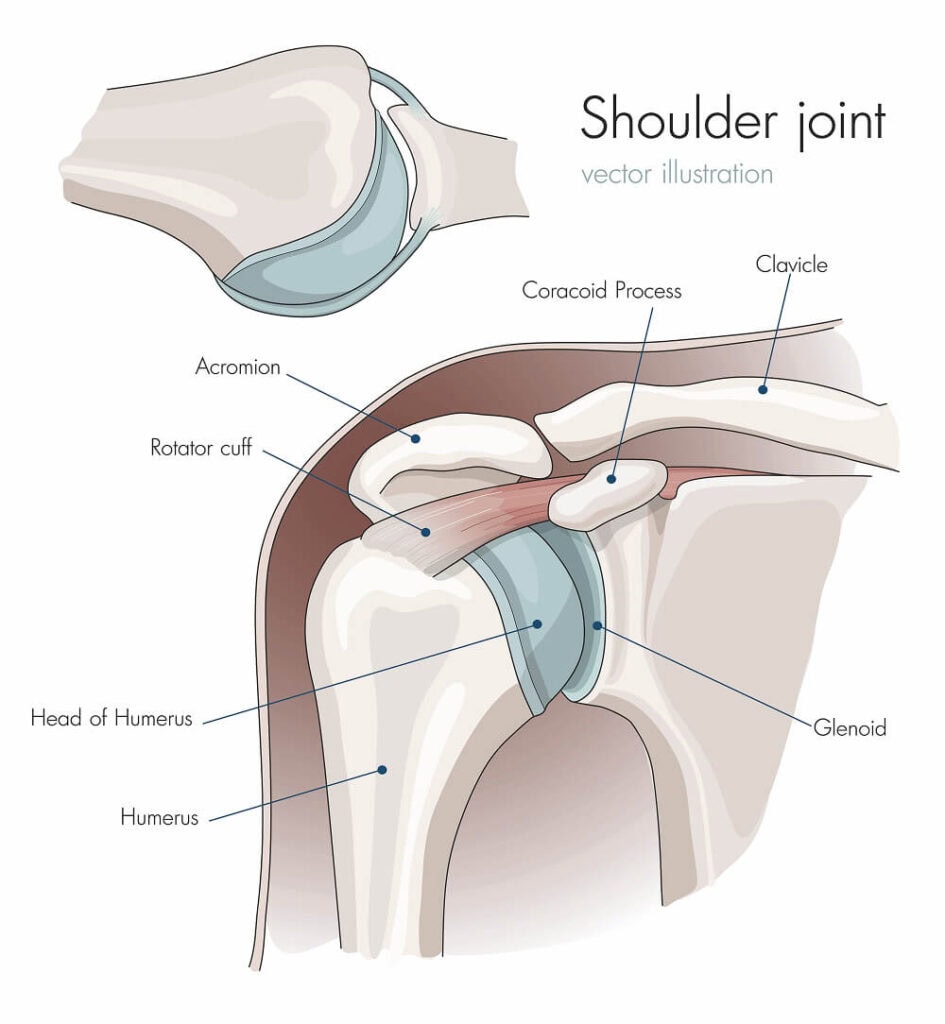
Key components of the shoulder include:
- Bones: The shoulder is formed by three main bones:
- The humerus (upper arm bone)
- The scapula (shoulder blade)
- The clavicle (collarbone)
- Joints: The shoulder has two main joints:
- The glenohumeral joint connects the humerus to the scapula. It forms the ball-and-socket structure that allows motions like rotating the arm and reaching overhead.
- The acromioclavicular (AC) joint connects the clavicle to the scapula. It provides stability during arm movements.
- There are two more smaller joints: the scapulothoracic and sternoclavicular joints. The scapulothoracic joint is an articulation between the scapula and the thoracic rib cage, allowing smooth shoulder elevation movements. The sternoclavicular joint connects the clavicle to the sternum, helping with shoulder stability and movement.
- Muscles and tendons: The shoulder’s joints are supported by ligaments and tendons connecting the surrounding muscles. These strong tissues are essential for mobility and stability, ensuring the shoulder joint remains properly aligned and helping to prevent injuries such as dislocations.
What Is A Torn Rotator Cuff?
The rotator cuff consists of four muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder’s ball-and-socket joint, keeping the upper arm bone securely within the glenoid cavity of the scapula (the socket). This ensures smooth, controlled movements when lifting, rotating, or extending the arm.
In addition to providing stability, the rotator cuff also helps with:
- Lifting the arm
- Rotating the arm both internally and externally
- Maintaining shoulder stability during dynamic movements
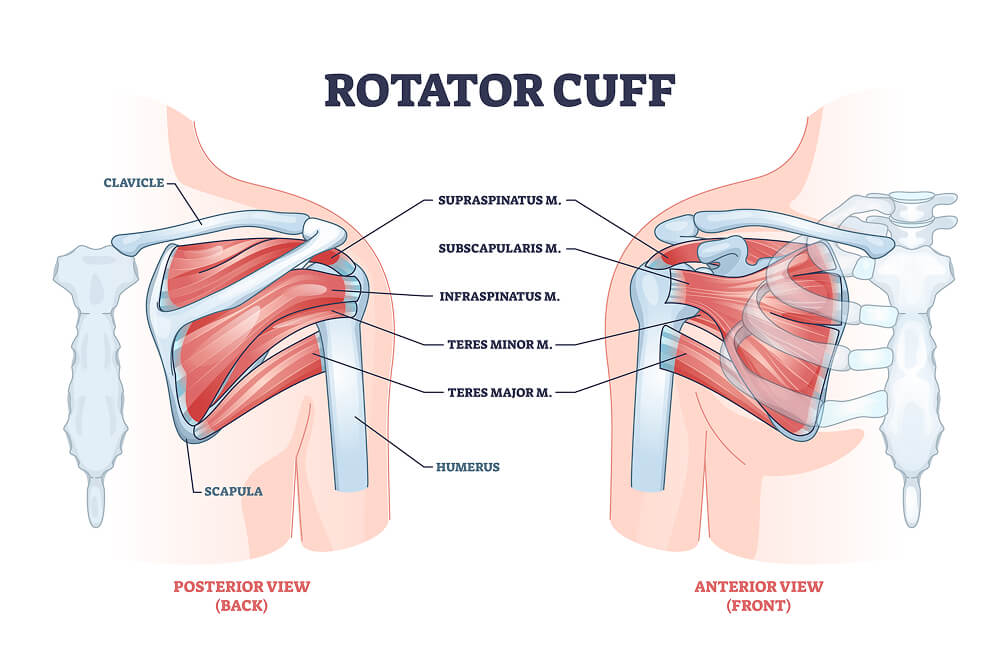
The four key muscles and tendons in the rotator cuff are:
- Supraspinatus: Located at the top of the shoulder, this muscle helps lift the arm to the side (abduction).
- Infraspinatus: Positioned at the back of the shoulder, it aids in the external rotation of the arm.
- Teres minor: A small muscle below the infraspinatus, also responsible for external rotation.
- Subscapularis: Found at the front of the shoulder, this muscle allows for internal arm rotation.
Types Of Tears In The Rotator Cuff
Rotator cuff tears happen when the tendons connecting the shoulder muscles to the bones degenerate or tear. These tears can result from overuse, injury, or age-related wear, impairing shoulder mobility and function.
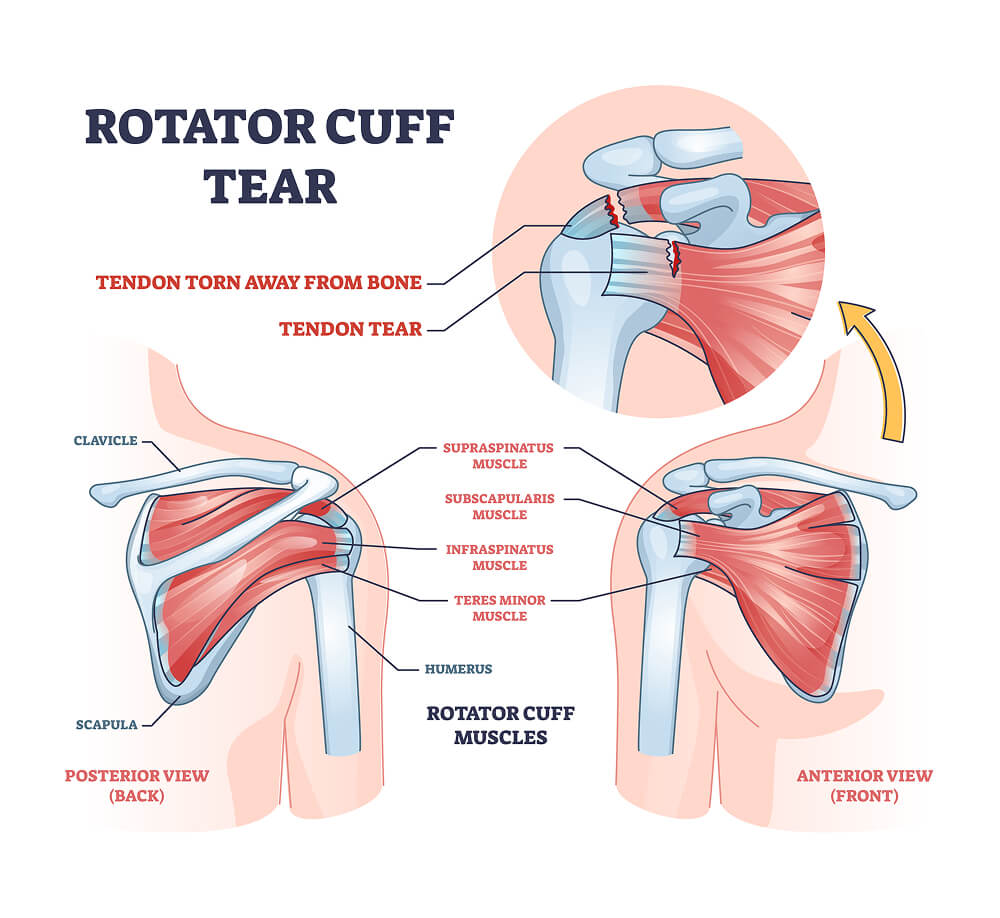
Rotator cuff tears are categorized by the extent of damage to the tendon:
- Partial-thickness or incomplete tear: A partial tear involves damage to the tendon without fully severing it. In this type, a portion of the tendon’s thickness is torn, but the tendon remains attached. This can cause pain and difficulty with shoulder movement, though some function is retained.
- Full-thickness or complete tear: A full-thickness tear is a complete tear through the tendon. This type of tear typically results in significant pain, loss of shoulder function, and weakness. Normal shoulder movement becomes difficult or impossible without the tendon attached, often requiring medical intervention for recovery.
Left untreated, full-thickness tears can lead to long-term complications, such as muscle atrophy and joint degeneration.
Who Is At Risk Of A Torn Rotator Cuff?
Rotator cuff tears can affect anyone, but certain factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing one:
- Poor posture: Poor posture, such as slouching or rounded shoulders, can place extra strain on the rotator cuff. Over time, muscle imbalances and uneven wear of the shoulder joints can increase injury risk. A 2015 study found that rotator cuff tears occurred in approximately 56% of individuals with poor posture, compared to 2.9% in those with good posture.
- Family history: Some people may be predisposed to tendon weakness or degeneration, making them more susceptible to rotator cuff injuries. A 2017 systematic review reports that around a third of patients with rotator cuff tears had family members with a history of this condition.
- People aged 40 or older: With aging, the tendons in the shoulder naturally weaken and lose elasticity, increasing the likelihood of tears.
- Athletes or workers with repetitive shoulder movements: People involved in activities that require repetitive overhead motions, such as athletes (e.g., swimmers, baseball players) or laborers (e.g., painters, carpenters), are at higher risk of rotator cuff tears due to constant strain on the shoulder joint.
Rotator cuff problems may be more common in women than men due to increased joint mobility and a higher risk of osteoarthritis. A study of 1,003 women aged 64-87 found that 22% had rotator cuff tears, with the prevalence increasing with age and more commonly affecting the dominant arm.
Causes Of A Torn Rotator Cuff
There are two types of rotator cuff tears:
- Acute tears: These occur suddenly, usually due to trauma or injury, such as a fall, direct impact, or lifting something too heavy.
- Degenerative tears: These develop slowly over time, often due to age-related wear or repetitive movements that cause the tendons to weaken and become brittle.
Common causes for rotator cuff tears include:
Repetitive Overhead Activities
Repetitive overhead movements are common in sports like swimming or baseball and occupations like painting. These motions place constant strain on the rotator cuff. Over time, this strain can increase the risk of tendon weakening and tearing, especially in the dominant arm.
Trauma And Injury
Direct trauma, such as a fall or a sudden heavy lift, can cause an acute rotator cuff tear. This is more likely in individuals with pre-existing tendon damage or weakening and those playing contact sports. Injuries may result in immediate pain and the inability to lift the arm.
Lack Of Blood Supply
As people age, the blood supply to the rotator cuff tendons decreases, limiting the body’s ability to repair damage. Reduced blood flow can cause the tendons to weaken over time, increasing the risk of degenerative tears, particularly in individuals over 50.
Signs And Symptoms Of A Torn Rotator Cuff
A 2021 study suggests that around half of rotator cuff tears are asymptomatic. However, symptoms vary depending on the severity of the injury and may progress over time. These include:
Pain And Swelling
Pain from a rotator cuff tear is typically felt in the front and side of the shoulder. It may also radiate down the arm, towards the elbow. Patients often report that pain worsens with certain movements, such as reaching overhead, lifting objects, or lying on the affected side.
In some cases, the pain can extend into the neck or back. This can happen when other structures compensate for shoulder weakness.
The intensity and location of the pain can vary depending on the severity of the tear and whether the injury is acute or degenerative. Additionally, pain can be accompanied by swelling, which occurs due to inflammation in the shoulder joint, leading to the accumulation of fluid in the surrounding tissues.
Muscle Weakness
Torn rotator cuff tendons may be unable to support the shoulder muscles properly, leading to a loss of strength. This weakness can interfere with lifting objects or performing tasks requiring arm strength, affecting overall arm function.
Limited Range Of Motion
A torn rotator cuff can reduce the shoulder’s range of motion. Swelling and pain can make movement difficult and undesirable. Over time, mobility can become increasingly restricted, hindering movements like reaching overhead or behind the back.
Diagnosis And Evaluation Procedure
A physician may use several tools to identify rotator cuff tears and rule out other conditions. These include:
- Medical history inquiry. A physician may assess past injuries, illnesses, and activity levels to determine the cause of shoulder pain. This information is crucial in identifying patterns, genetic factors, or pre-existing conditions that might contribute to a tear.
- Physical examination. Physical exams involve assessing shoulder strength and range of motion. Doctors check for pain points and perform specific movements to locate the tear.
- X-ray. X-rays provide images of hard tissues like bones. They can detect bone spurs or other issues affecting the rotator cuff. Although X-rays can’t show soft-tissue damage directly, they may help rule out fractures and other bone problems.
- MRI. MRI scans offer detailed images of soft tissues, including muscles and tendons. They can show the extent of the rotator cuff tear, its location, and any associated inflammation or damage.
- Ultrasound. Physicians may use ultrasound to create real-time images of the shoulder’s soft tissues. This tool can help assess tendon movement to identify tears, inflammation, and other issues.
Conventional Treatment Options Available
Treatment for rotator cuff tears depends on the severity. At-home care often manages mild tears, while severe cases may require more complex treatments. The goal is to alleviate pain, improve shoulder function, and prevent further damage.
Common treatments include:
- Medications: Medications may help manage pain temporarily. However, shoulder conditions like rotator cuff tears are often long-term. One study reports that over 40% of patients visiting a physician with shoulder pain were still experiencing symptoms 12 months later. Relying on medications for such extended periods can lead to severe side effects and let the underlying cause of pain go untreated. As damage to the rotator cuff and shoulder components progresses, the risk of requiring surgery increases.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy involves exercises that strengthen shoulder muscles and improve flexibility. Therapists often use techniques like ultrasound or electrical stimulation to enhance treatment. This approach supports joint stability and function but requires consistent efforts over time.
- Surgery: Surgery is sometimes considered when non-invasive treatments fail to relieve symptoms or in cases of severe rotator cuff tears. The goal is to restore shoulder function and alleviate persistent pain. However, surgical procedures carry risks, and the results may vary depending on the patient’s condition. The 2021 study also found that even patients with full-thickness rotator cuff tears can achieve and maintain improved shoulder function and reduced pain without surgery.
- Arthroscopic Tendon Repair: Arthroscopic tendon repair involves small incisions through which a camera and instruments are inserted to repair the tear. It is less invasive and leads to shorter recovery times than other surgical procedures. However, it carries risks, including infection, stiffness, and incomplete healing.
- Open Tendon Repair: Open tendon repair requires a larger incision to access and repair the tear directly. This method allows for more extensive repairs but has a longer recovery period. Risks involve higher chances of infection, blood loss, and prolonged shoulder stiffness. While open tendon repair can provide extensive repairs, there is a risk of complications. A 2021 study found that re-tear rates range from 13.1% to 79%, depending on patient age, tear size, and rehabilitation protocols.
- Shoulder Replacement: Shoulder replacement involves replacing damaged shoulder components with artificial ones. This major surgery carries risks, including infections and implant issues, and requires long-term rehabilitation. It is typically reserved for cases where large tears and arthritis have caused significant loss of shoulder function, chronic pain, or disability.
We Are Redefining Shoulder Care With Our Non-Surgical Solutions
In some cases, rotator cuff tears can be managed by enhancing the body’s natural healing process. The Regenexx approach uses interventional orthobiologics to provide a non-surgical alternative to conventional treatments such as medications or surgery.
The nature and severity of the rotator cuff tear (its classification type) help the physician determine if the treatment may be right for your condition. An evaluation by a physician in the licensed Regenexx network is the first step.
Customized treatment plans may include one or more of the orthobiologics procedures below.
Regenexx SD Injectate
Procedures using Regenexx SD injectate include a patented protocol that utilizes Bone Marrow Concentrate (BMC), which contains the patient’s own mesenchymal stem cells. The cell processing for a Regenexx SD injectate routinely achieves 20x concentration— far above what non-Regenexx cell processing can achieve.
Regenexx SCP Injectate
Procedures using Regenexx SCP injectate represent a supercharged platelet-rich plasma (PRP) version. In this process, blood is drawn and then processed to isolate the platelets and growth factors. The growth factors are then purified, concentrated, and injected into the shoulder area using imaging guidance for precision. Regenexx-SCP injectate provides a higher concentration of growth factors than typical PRP procedures.
Regenexx PL Injectate
Regenexx PL injectate procedures are a highly specialized derivative of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) with a faster and more concentrated release of growth factors compared to typical PRP. The PL injectate is often combined with other orthobiologics such as PRP and bone marrow concentrate.
The Benefits Of The Regenexx Approach
Using the industry-leading SANS evaluation method, physicians in the licensed Regenexx network can examine the body in motion–including the shoulder, neck, and nearby nerves–and review existing imaging (MRI and/or X-ray). They also often use ultrasound to observe the inner workings of the joint in real-time.
Combined, these evaluation methods allow physicians in the licensed Regenexx network to get a more accurate picture of what contributes to symptoms, how the function has been affected, and, ultimately, the root cause of pain.
Physicians can then use this knowledge to design customized treatment plans based on each patient’s injury. Procedures using Regenexx lab processes help harness the body’s natural healing ability. Using interventional orthobiologics, the Regenexx approach offers an alternative to surgery and may reduce the need for prescription drugs, such as opioids.
What Happens When A Rotator Cuff Tear Is Left Untreated
When rotator cuff tears are left untreated, they may lead to complications such as chronic pain and shoulder joint damage, restricted mobility, decreased function, and loss of muscle strength. Prolonged untreated tears can lead to arthritis or other joint issues, and the risk of surgery increases as the tear worsens.
Learn how a physician in the licensed Regenexx network may be able to help address your rotator cuff tear without surgery.
Get started to see if you are a Regenexx candidate
To talk one-on-one with one of our team members about how the Regenexx approach may be able to help your orthopedic pain or injury, please complete the form below and we will be in touch with you within the next business day.

Medically Reviewed By:
