Intersection Syndrome: What You Need To Know

Medically Reviewed By:
Intersection syndrome is a condition that affects the first and second compartments of the dorsal wrist extensors, leading to pain and inflammation in the forearm near the wrist. The condition occurs when tendons become irritated as they cross over each other, often due to repetitive motions like rowing, lifting, or typing.
The incidence of intersection syndrome ranges from 0.2% to 0.37%, making it a relatively uncommon condition. Individuals typically experience swelling, discomfort, and difficulty with tasks that involve wrist and forearm movement. This guide explores the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What Is Intersection Syndrome?
Intersection syndrome develops when inflammation occurs in the tendons on the back (thumb side) of the wrist, where two compartments containing tendons intersect. The condition primarily affects the forearm area just above the wrist.
The inflammation impacts wrist and forearm function, often due to repetitive motion. Intersection syndrome is a type of tenosynovitis. Understanding the anatomical structure of the tendons and their location aids in diagnosing and managing the condition.
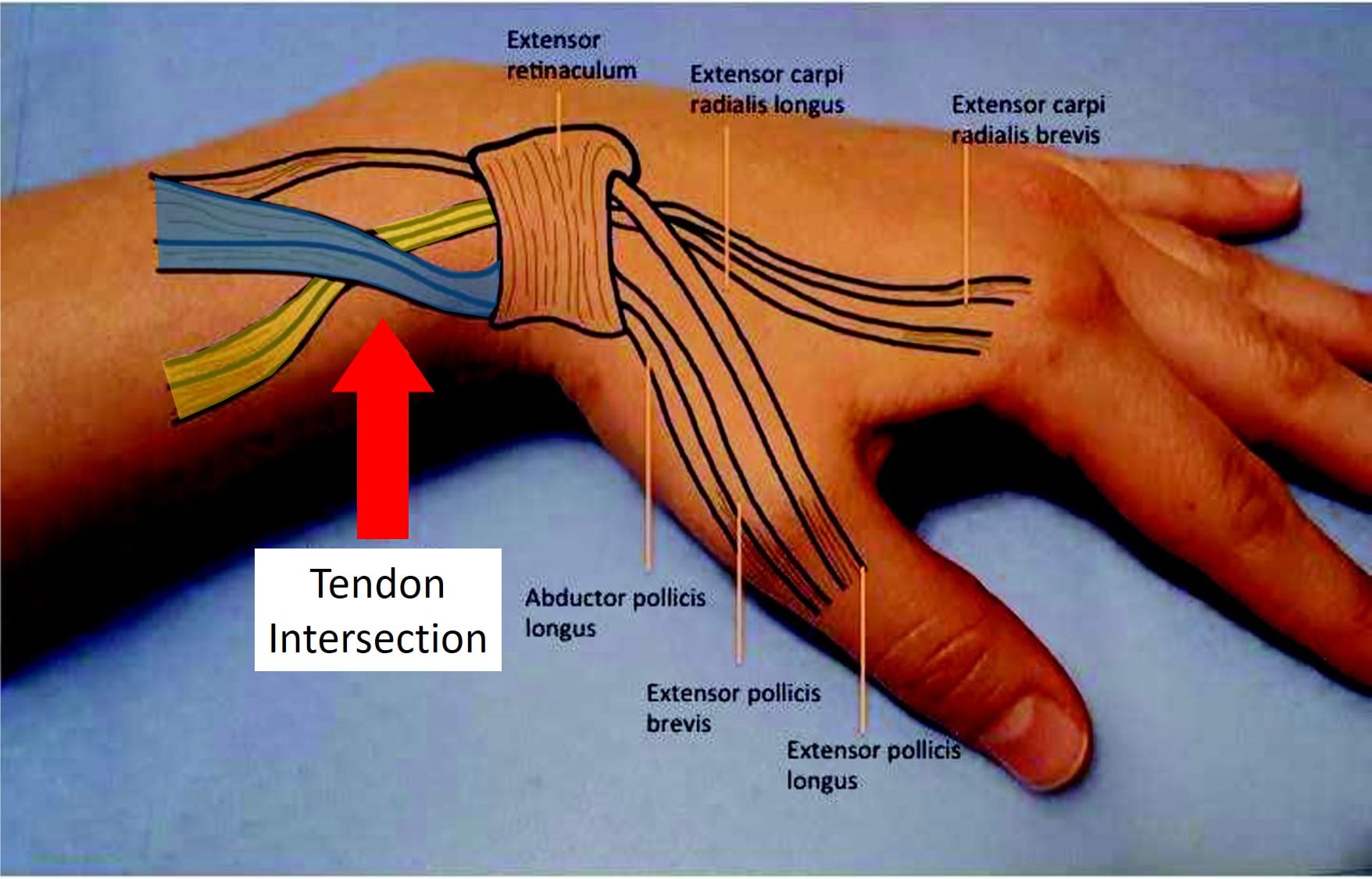
Anatomical Structures Behind Tendon Inflammation
Intersection syndrome affects specific tendons on the thumb side of the wrist, particularly those responsible for extending the hand or moving it towards the thumb (radially).
This intersection occurs where the tendons of the first and second dorsal wrist compartments meet, specifically where the abductor pollicis longus (APL) and extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) tendons cross over the extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL) and extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) tendons.
At the intersection point, the tendons of the APL and EPB cross over the tendons of the ECRL and ECRB. This crossing occurs just above the wrist, where inflammation and irritation can develop due to mechanical friction and repetitive motion.
Visualizing the intersection can clarify how repetitive wrist movements lead to tendon irritation and inflammation.
Repetitive Motion And Other Causes of Tendon Irritation
One challenge in diagnosing intersection syndrome is that it primarily describes the pain or swelling’s location rather than identifying the actual cause.
The root causes of intersection syndrome can vary.
- Ligament Damage: The ligaments holding the small carpal bones in the wrist may become damaged, allowing excessive bone movement that irritates the tendons at the intersection point.
- Nerve Irritation: Spinal nerve irritation in the neck can cause muscles attached to these tendons to misfire, increasing strain. Addressing neck issues may require treatments such as guided injections to alleviate the nerve irritation.
See the video below for more information.
Contributing Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of tendon irritation:
- Age: Tendons lose flexibility and strength over time, making them more prone to irritation.
- Occupational hazards: Jobs requiring repetitive wrist movements, such as typing or manual labor, can increase the risk of tendon strain. Examples include office work, construction, and assembly-line tasks.
- Sports-related risks: Activities like rowing, skiing, or weightlifting involve repetitive wrist motions that can lead to inflammation.
Symptoms That Indicate Repetitive Strain in the Wrist
Symptoms of repetitive strain include:
- Pain radiating to wrist and forearm: This pain, which may worsen with activity, can make everyday tasks challenging.
- Tenderness or swelling: Pressing the affected area near the intersection of tendons may reveal tenderness or swelling.
- Grinding sensation: Inflamed tendons rubbing against each other can create a squeaking or grinding sensation.
- Limited range of motion: Difficulty fully extending or flexing the hand may develop as the condition worsens.
Methods For Diagnosing The Condition
Diagnosing intersection syndrome involves:
- Physical examination: Physicians check for swelling, tenderness, and grinding sensations in the wrist near the intersection of tendons.
- Imaging: Ultrasound effectively detects tendon swelling, while MRI assesses inflammation. X-rays and CT scans are less useful as they do not visualize tendons.
Treatment Methods For Tendon Overuse
Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation, managing pain, and promoting tendon healing:
- Activity modification: Resting the wrist and avoiding repetitive movements allows the tendons to recover.
- Splinting or bracing: A wrist brace can limit excessive movement and irritation.
- Physical therapy: Exercises can strengthen surrounding muscles and improve flexibility.
- Surgery: Rarely, a tenosynovectomy removes the inflamed tendon sheath, though this may disrupt normal tendon function.
Getting An Accurate Diagnosis
Physicians in the licensed Regenexx network may use advanced tools like ultrasound and the SANS evaluation method to analyze joint health.
These techniques assist in diagnosing conditions accurately by identifying tendon issues and ruling out other causes of wrist pain. During the evaluation, physicians review existing imaging and may incorporate advanced diagnostic tools, such as ultrasound, MRI, or both, to determine the sources of pain.
Explore Non-Surgical Options For Pain And Mobility
The Regenexx approach offers a non-surgical option for managing symptoms associated with intersection syndrome. Injectates using Regenexx lab processes utilize interventional orthobiologics to support the body’s natural healing abilities. This approach provides a less invasive alternative to surgery or reliance on long-term prescription medications, such as opioids.
Consult a physician in the licensed Regenexx network to find out if Regenexx’s proprietary methods may help reduce pain and improve mobility.
Get started to see if you are a Regenexx candidate
To talk one-on-one with one of our team members about how the Regenexx approach may be able to help your orthopedic pain or injury, please complete the form below and we will be in touch with you within the next business day.

Medically Reviewed By:
