LOL AAOS! You Guys Crack Me Up – More Steroids and Less PRP for Knees!

Credit: Shutterstock
It’s official, the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons is now officially off its collective rocker. Instead of adding PRP to their knee arthritis treatment guidelines, which would be an evidence-based thing to do in 2021, the AAOS has avoided all evidence and doubled down on the ridiculous practice of injecting steroids into knees! However, wait, it gets far worse and more humorous than that, so let’s dig into the wacky new “guidelines”.
The New 2021 AAOS Knee OA Guidelines
I was first introduced to the new American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (AAOS) knee osteoarthritis guidelines by a story in an orthopedics mag that looks like it was sponsored by the makers of Zilretta (1). What’s that? It’s a long-acting high-dose steroid medication used to treat the symptoms of knee OA.
The article stated:
“With changes to 19 of the 29 recommendations from the previous guideline, the new document focused only on less invasive non-arthoplasty treatments. Notably, the guidelines mentioned a relatively new treatment, a time-release corticosteroid, Zilretta®.”
Given that we now know for sure that high-dose corticosteroids destroy knee cartilage, why would anyone invent a long-acting high-dose steroid? Your guess is as good as mine. Hence, this launched me on a journey to investigate more about these guideline changes and guess what folks, I was not disappointed by the AAOS’s nutty new document.
You Can’t Make This Stuff Up
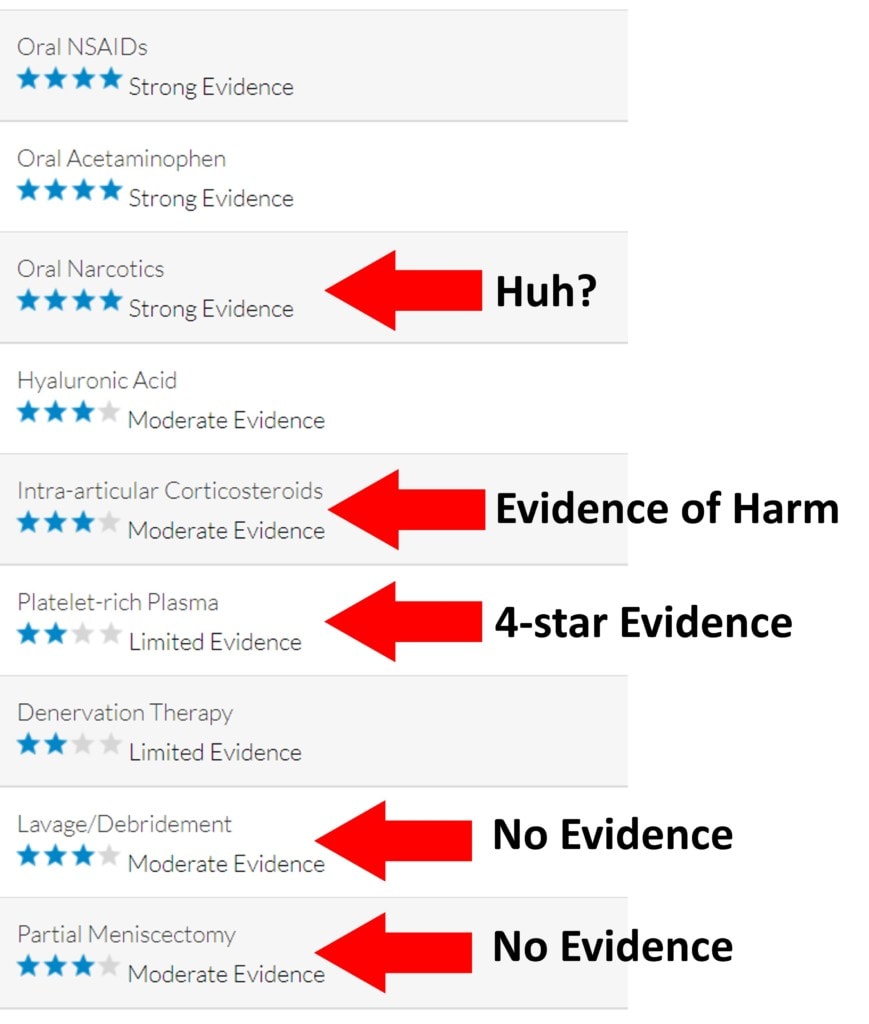
The latest knee arthritis guidelines from the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons came out at the end of August 2021 (62). As you can see above, the AAOS guidelines committee used a star system to grade the evidence in favor of using various treatments for knee arthritis. That makes sense because many people are used to seeing a similar system to rate everything from hotels to doctors online. What makes no sense is the shenanigans that the surgeons used to prop up the treatments that create chunks of orthopedic surgical income and suppress the ones that don’t.
Let’s dig into this buffet of self-dealing and ignoring the actual published evidence. First, you can’t look away from the train wreck that is the three-star recommendation for using a partial meniscectomy to treat knee OA. We have three large randomized controlled trials that show that the procedure is no better than a sham surgery or physical therapy (2-4). Hence, that’s not moderate evidence of efficacy as is claimed, that’s evidence of lack of efficacy. Add to that the fact that most meniscus tears in middle-aged and elderly people represent normal aging and you have a guidelines committee that must have squinted pretty hard and said three hail Marys while doing the sign of the cross to call this “moderate evidence” (5).
Another ridiculous assertion is that “lavage/debridement” is a 3-star treatment for knee arthritis. We know this isn’t even close to true as that procedure was determined to be no better than the placebo way back in 2002! (10) A 2013 article published in the American Journal of Sports Medicine noted that there was already a 39% drop in that surgery based on that then decade-old paper (11). So here we are, almost two decades after Moseley’s groundbreaking research showing that this surgery was no more effective than a faked procedure and AAOS is claiming that there is moderate evidence to support its use? In what universe is that true?
Next up is corticosteroids. These are the steroid injections given by surgeons to people with knee arthritis. As discussed above, we know that the steroid that Zilretta is based on, triamcinolone, is a high-dose anti-inflammatory. This is the most commonly injected knee steroid medication that we know destroys cartilage based on a randomized controlled trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (6). Again, that’s not moderate evidence of efficacy, that’s four-star evidence of harm.
You also can’t look away from the pharma-sponsored aspects of this guideline, which are frankly a slap in the face of the opioid crisis that has killed almost a million Americans since the first high-dose opioids were introduced (7). Meaning the AAOS lists “Oral Narcotics” as a 4-star treatment for knee arthritis? That’s bizarre as a 2016 meta-analysis clearly showed that NSAIDs worked about as well for knee OA pain as narcotics (8). While NSAIDs have their own issues with increasing cardiac sudden death risk, at least they don’t leave you physically addicted (9)!
PRP Is a 2-Star Therapy?
As I have written many times before, we have much more evidence that PRP is effective to treat knee arthritis than any orthopedic surgery including knee replacement, partial meniscectomy, or lavage/debridement. In fact, there are dozens of RCTs showing that PRP is effective for knee osteoarthritis and many more showing it’s effective in other orthopedic conditions (12-61). This evidence is against a backdrop showing that few orthopedic surgeries have basic evidence that they’re more effective than doing nothing or conservative care (62). In fact, I created a table from that seminal British Medical Journal systematic review:

Why Am I So Hard on My Orthopedic Surgery Colleagues?
I get flack all the time from various orthopedic surgeons I know concerning the fact that I am much too hard on surgeons. However, looking at this AAOS guideline, is there any wonder why? This thing is so bad and so divorced from what’s published in the medical literature that its theater of the absurd. So listen up surgical boys and girls, you want respect? Earn it by actually letting the evidence drive your surgical decision-making.
The upshot? This guideline is insane. It basically says we need more discredited surgeries with no evidence of efficacy, more steroids to kill cartilage, and we’ll throw in some high-dose narcotics that cause addiction just for fun! Is it any wonder I’m critical of this specialty? It’s stuff like this, ignoring surgical outcomes, that has forced patients in droves to look for surgical alternatives.
___________________________________
References:
(1) Orthopedics this Week. AAOS UPDATES KNEE OA GUIDELINE, HIGHLIGHTS ZILRETTA® Accessed 10/17/21 https://ryortho.com/breaking/aaos-updates-knee-oa-guideline-highlights-zilretta/
(2) Finnish Degenerative Meniscal Lesion Study (FIDELITY) Group. Arthroscopic Partial Meniscectomy versus Sham Surgery for a Degenerative Meniscal Tear. N Engl J Med 2013; 369:2515-2524
(12) Senna MK, Shaat RM, Ali AAA. Platelet-rich plasma in treatment of patients with idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin Rheumatol. 2019 Dec;38(12):3643-3654. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04719-7. Epub 2019 Aug 16. PMID: 31420812.
(13) Kesikburun S, Tan AK, Yilmaz B, Yaşar E, Yazicioğlu K. Platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2013 Nov;41(11):2609-16. doi: 10.1177/0363546513496542. Epub 2013 Jul 26. PMID: 23893418.
(14) Malahias MA, Nikolaou VS, Johnson EO, Kaseta MK, Kazas ST, Babis GC. Platelet-rich plasma ultrasound-guided injection in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: A placebo-controlled clinical study. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018 Mar;12(3):e1480-e1488. doi: 10.1002/term.2566. Epub 2017 Dec 17. PMID: 28873284.
(15) Malahias MA, Nikolaou VS, Johnson EO, Kaseta MK, Kazas ST, Babis GC. Platelet-rich plasma ultrasound-guided injection in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: A placebo-controlled clinical study. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018 Mar;12(3):e1480-e1488. doi: 10.1002/term.2566. Epub 2017 Dec 17. PMID: 28873284.
(16) Uslu Güvendi E, Aşkin A, Güvendi G, Koçyiğit H. Comparison of Efficiency Between Corticosteroid and Platelet Rich Plasma Injection Therapies in Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis. Arch Rheumatol. 2017;33(3):273–281. Published 2017 Nov 2. doi: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2018.6608
(17) Tavassoli M, Janmohammadi N, Hosseini A, Khafri S, Esmaeilnejad-Ganji SM. Single- and double-dose of platelet-rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid for treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. World J Orthop. 2019;10(9):310–326. Published 2019 Sep 18. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v10.i9.310
(18) Joshi Jubert N, Rodríguez L, Reverté-Vinaixa MM, Navarro A. Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections for Advanced Knee Osteoarthritis: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial. Orthop J Sports Med. 2017;5(2):2325967116689386. Published 2017 Feb 13. doi: 10.1177/2325967116689386
(19) Raeissadat SA, Rayegani SM, Hassanabadi H, et al. Knee Osteoarthritis Injection Choices: Platelet- Rich Plasma (PRP) Versus Hyaluronic Acid (A one-year randomized clinical trial). Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;8:1–8. Published 2015 Jan 7. doi: 10.4137/CMAMD.S17894
(20) Montañez-Heredia E, Irízar S, Huertas PJ, et al. Intra-Articular Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma versus Hyaluronic Acid in the Treatment of Osteoarthritic Knee Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial in the Context of the Spanish National Health Care System. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(7):1064. Published 2016 Jul 2. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071064
(21) Görmeli G, Görmeli CA, Ataoglu B, Çolak C, Aslantürk O, Ertem K. Multiple PRP injections are more effective than single injections and hyaluronic acid in knees with early osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017 Mar;25(3):958-965. doi: 10.1007/s00167-015-3705-6.
(22) Lana JF, Weglein A, Sampson SE, et al. Randomized controlled trial comparing hyaluronic acid, platelet-rich plasma and the combination of both in the treatment of mild and moderate osteoarthritis of the knee. J Stem Cells Regen Med. 2016;12(2):69–78. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5227106/
(23) Tavassoli M, Janmohammadi N, Hosseini A, Khafri S, Esmaeilnejad-Ganji SM. Single- and double-dose of platelet-rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid for treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. World J Orthop. 2019;10(9):310–326. Published 2019 Sep 18. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v10.i9.310
(24) Lin KY, Yang CC, Hsu CJ, Yeh ML, Renn JH. Intra-articular Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma Is Superior to Hyaluronic Acid or Saline Solution in the Treatment of Mild to Moderate Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Triple-Parallel, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Arthroscopy. 2019 Jan;35(1):106-117. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2018.06.035.
(25) Huang Y, Liu X, Xu X, Liu J. Intra-articular injections of platelet-rich plasma, hyaluronic acid or corticosteroids for knee osteoarthritis : A prospective randomized controlled study. Orthopade. 2019 Mar;48(3):239-247. doi: 10.1007/s00132-018-03659-5.
(26) Di Martino A, Di Matteo B, Papio T, Tentoni F, Selleri F, Cenacchi A, Kon E, Filardo G. Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Hyaluronic Acid Injections for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: Results at 5 Years of a Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Am J Sports Med. 2019 Feb;47(2):347-354. doi: 10.1177/0363546518814532.
(27) Yu W, Xu P, Huang G, Liu L. Clinical therapy of hyaluronic acid combined with platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(3):2119–2125. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6412
(28) Buendía-López D, Medina-Quirós M, Fernández-Villacañas Marín MÁ. Clinical and radiographic comparison of a single LP-PRP injection, a single hyaluronic acid injection and daily NSAID administration with a 52-week follow-up: a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Traumatol. 2018;19(1):3. Published 2018 Aug 20. doi: 10.1186/s10195-018-0501-3
(29) Su K, Bai Y, Wang J, Zhang H, Liu H, Ma S. Comparison of hyaluronic acid and PRP intra-articular injection with combined intra-articular and intraosseous PRP injections to treat patients with knee osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2018 May;37(5):1341-1350. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-3985-6.
(30) Louis ML, Magalon J, Jouve E, Bornet CE, Mattei JC, Chagnaud C, Rochwerger A, Veran J3, Sabatier F. Growth Factors Levels Determine Efficacy of Platelets Rich Plasma Injection in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Double Blind Noninferiority Trial Compared With Viscosupplementation. Arthroscopy. 2018 May;34(5):1530-1540.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2017.11.035.
(31) Lisi C, Perotti C, Scudeller L, Sammarchi L, Dametti F, Musella V, Di Natali G. Treatment of knee osteoarthritis: platelet-derived growth factors vs. hyaluronic acid. A randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2018 Mar;32(3):330-339. doi: 10.1177/0269215517724193
(32) Cole BJ, Karas V, Hussey K, Pilz K, Fortier LA. Hyaluronic Acid Versus Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Prospective, Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Clinical Outcomes and Effects on Intra-articular Biology for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Am J Sports Med. 2017 Feb;45(2):339-346. doi: 10.1177/0363546516665809.
(33) Kaminski R, Maksymowicz-Wleklik M, Kulinski K, Kozar-Kaminska K, Dabrowska-Thing A, Pomianowski S. Short-Term Outcomes of Percutaneous Trephination with a Platelet Rich Plasma Intrameniscal Injection for the Repair of Degenerative Meniscal Lesions. A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group, Placebo-Controlled Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 16;20(4):856. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040856. PMID: 30781461; PMCID: PMC6412887.
(34) Malahias MA, Roumeliotis L, Nikolaou VS, Chronopoulos E, Sourlas I, Babis GC. Platelet-Rich Plasma versus Corticosteroid Intra-Articular Injections for the Treatment of Trapeziometacarpal Arthritis: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Cartilage. 2021 Jan;12(1):51-61. doi: 10.1177/1947603518805230. Epub 2018 Oct 20. PMID: 30343590; PMCID: PMC7755966.
(35) Dallari D, Stagni C, Rani N, Sabbioni G, Pelotti P, Torricelli P, Tschon M, Giavaresi G. Ultrasound-Guided Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Hyaluronic Acid, Separately and in Combination, for Hip Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Study. Am J Sports Med. 2016 Mar;44(3):664-71. doi: 10.1177/0363546515620383. Epub 2016 Jan 21. PMID: 26797697.
(36) Battaglia M, Guaraldi F, Vannini F, Rossi G, Timoncini A, Buda R, Giannini S. Efficacy of ultrasound-guided intra-articular injections of platelet-rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid for hip osteoarthritis. Orthopedics. 2013 Dec;36(12):e1501-8. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20131120-13. PMID: 24579221.
(37) Pasin T, Ataoğlu S, Pasin Ö, Ankarali H. Comparison of the Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma, Corticosteroid, and Physical Therapy in Subacromial Impingement Syndrome. Arch Rheumatol. 2019 Mar 28;34(3):308-316. doi: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2019.7225. PMID: 31598597; PMCID: PMC6768781.
(38) Shams A, El-Sayed M, Gamal O, Ewes W. Subacromial injection of autologous platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid for the treatment of symptomatic partial rotator cuff tears. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2016 Dec;26(8):837-842. doi: 10.1007/s00590-016-1826-3. Epub 2016 Aug 20. PMID: 27544678.
(39) Kesikburun S, Tan AK, Yilmaz B, Yaşar E, Yazicioğlu K. Platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2013 Nov;41(11):2609-16. doi: 10.1177/0363546513496542. Epub 2013 Jul 26. PMID: 23893418.
(40) Cai YU, Sun Z, Liao B, Song Z, Xiao T, Zhu P. Sodium Hyaluronate and Platelet-Rich Plasma for Partial-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019;51(2):227-233. doi:10.1249/MSS.0000000000001781
(41) Lin J. Platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of frozen shoulder: A randomized controlled trial with 6-month follow-up . Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Aug;56(8):366-371. doi: 10.5414/CP203262. PMID: 29932415.
(42) Nejati P, Ghahremaninia A, Naderi F, Gharibzadeh S, Mazaherinezhad A. Treatment of Subacromial Impingement Syndrome: Platelet-Rich Plasma or Exercise Therapy? A Randomized Controlled Trial. Orthop J Sports Med. 2017 May 19;5(5):2325967117702366. doi: 10.1177/2325967117702366. PMID: 28567426; PMCID: PMC5439655.
(43) Pasin T, Ataoğlu S, Pasin Ö, Ankarali H. Comparison of the Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma, Corticosteroid, and Physical Therapy in Subacromial Impingement Syndrome. Arch Rheumatol. 2019 Mar 28;34(3):308-316. doi: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2019.7225. PMID: 31598597; PMCID: PMC6768781.
(44) Rha DW, Park GY, Kim YK, Kim MT, Lee SC. Comparison of the therapeutic effects of ultrasound-guided platelet-rich plasma injection and dry needling in rotator cuff disease: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2013 Feb;27(2):113-22. doi: 10.1177/0269215512448388. Epub 2012 Oct 3. PMID: 23035005.
(45) Senna MK, Shaat RM, Ali AAA. Platelet-rich plasma in treatment of patients with idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin Rheumatol. 2019 Dec;38(12):3643-3654. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04719-7. Epub 2019 Aug 16. PMID: 31420812.
(46) Pasin T, Ataoğlu S, Pasin Ö, Ankarali H. Comparison of the Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma, Corticosteroid, and Physical Therapy in Subacromial Impingement Syndrome. Arch Rheumatol. 2019 Mar 28;34(3):308-316. doi: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2019.7225. PMID: 31598597; PMCID: PMC6768781.
(47) Mishra AK, Skrepnik NV, Edwards SG, Jones GL, Sampson S, Vermillion DA, Ramsey ML, Karli DC, Rettig AC. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma for chronic tennis elbow: a double-blind, prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trial of 230 patients. Am J Sports Med. 2014 Feb;42(2):463-71. doi: 10.1177/0363546513494359. Epub 2013 Jul 3. PMID: 23825183.
(48) Pasin T, Ataoğlu S, Pasin Ö, Ankarali H. Comparison of the Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma, Corticosteroid, and Physical Therapy in Subacromial Impingement Syndrome. Arch Rheumatol. 2019 Mar 28;34(3):308-316. doi: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2019.7225. PMID: 31598597; PMCID: PMC6768781.
(49) Martínez-Montiel O, Valencia-Martinez G, Blanco-Bucio P, Villalobos-Campuzano C. Tratamiento de epicondilitis de codo con plasma rico en plaquetas versus corticosteroide local [Treatment of elbow epicondylitis with platelet rich plasma versus local corticosteroids]. Acta Ortop Mex. 2015 May-Jun;29(3):155-8. Spanish. PMID: 26999966.
(50) Palacio EP, Schiavetti RR, Kanematsu M, Ikeda TM, Mizobuchi RR, Galbiatti JA. Effects of platelet-rich plasma on lateral epicondylitis of the elbow: prospective randomized controlled trial. Rev Bras Ortop. 2016 Jan 13;51(1):90-5. doi: 10.1016/j.rboe.2015.03.014. PMID: 26962506; PMCID: PMC4767828.
(51) Pasin T, Ataoğlu S, Pasin Ö, Ankarali H. Comparison of the Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma, Corticosteroid, and Physical Therapy in Subacromial Impingement Syndrome. Arch Rheumatol. 2019 Mar 28;34(3):308-316. doi: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2019.7225. PMID: 31598597; PMCID: PMC6768781.
(52) Gautam VK, Verma S, Batra S, Bhatnagar N, Arora S. Platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection for recalcitrant lateral epicondylitis: clinical and ultrasonographic evaluation. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2015 Apr;23(1):1-5. doi: 10.1177/230949901502300101. PMID: 25920633.
(53) Gosens T, Peerbooms JC, van Laar W, den Oudsten BL. Ongoing positive effect of platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection in lateral epicondylitis: a double-blind randomized controlled trial with 2-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2011 Jun;39(6):1200-8. doi: 10.1177/0363546510397173. Epub 2011 Mar 21. PMID: 21422467.
(54) Merolla G, Dellabiancia F, Ricci A, Mussoni MP, Nucci S, Zanoli G, Paladini P, Porcellini G. Arthroscopic Debridement Versus Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection: A Prospective, Randomized, Comparative Study of Chronic Lateral Epicondylitis With a Nearly 2-Year Follow-Up. Arthroscopy. 2017 Jul;33(7):1320-1329. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2017.02.009. Epub 2017 Apr 19. PMID: 28433443.
(55) Raeissadat SA, Rayegani SM, Hassanabadi H, Rahimi R, Sedighipour L, Rostami K. Is Platelet-rich plasma superior to whole blood in the management of chronic tennis elbow: one year randomized clinical trial. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2014 Mar 18;6:12. doi: 10.1186/2052-1847-6-12. PMID: 24635909; PMCID: PMC4006635.
(56) Thanasas C, Papadimitriou G, Charalambidis C, Paraskevopoulos I, Papanikolaou A. Platelet-rich plasma versus autologous whole blood for the treatment of chronic lateral elbow epicondylitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Am J Sports Med. 2011 Oct;39(10):2130-4. doi: 10.1177/0363546511417113. Epub 2011 Aug 2. PMID: 21813443.
(57) Kesikburun S, Tan AK, Yilmaz B, Yaşar E, Yazicioğlu K. Platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2013 Nov;41(11):2609-16. doi: 10.1177/0363546513496542. Epub 2013 Jul 26. PMID: 23893418.
(58) Kesikburun S, Tan AK, Yilmaz B, Yaşar E, Yazicioğlu K. Platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2013 Nov;41(11):2609-16. doi: 10.1177/0363546513496542. Epub 2013 Jul 26. PMID: 23893418.
(59) Kesikburun S, Tan AK, Yilmaz B, Yaşar E, Yazicioğlu K. Platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2013 Nov;41(11):2609-16. doi: 10.1177/0363546513496542. Epub 2013 Jul 26. PMID: 23893418.
(60) Boesen AP, Hansen R, Boesen MI, Malliaras P, Langberg H. Effect of High-Volume Injection, Platelet-Rich Plasma, and Sham Treatment in Chronic Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy: A Randomized Double-Blinded Prospective Study. Am J Sports Med. 2017 Jul;45(9):2034-2043. doi: 10.1177/0363546517702862. Epub 2017 May 22. PMID: 28530451.
(61) Alsousou J, Thompson M, Harrison P, Willett K, Franklin S. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on healing tissues in acute ruptured Achilles tendon: a human immunohistochemistry study. Lancet. 2015 Feb 26;385 Suppl 1:S19. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60334-8. PMID: 26312841.
(62) Blom AW, Donovan RL, Beswick AD, Whitehouse MR, Kunutsor SK. Common elective orthopaedic procedures and their clinical effectiveness: umbrella review of level 1 evidence. BMJ. 2021 Jul 7;374:n1511. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n1511. PMID: 34233885.

If you have questions or comments about this blog post, please email us at [email protected]
NOTE: This blog post provides general information to help the reader better understand regenerative medicine, musculoskeletal health, and related subjects. All content provided in this blog, website, or any linked materials, including text, graphics, images, patient profiles, outcomes, and information, are not intended and should not be considered or used as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Please always consult with a professional and certified healthcare provider to discuss if a treatment is right for you.